
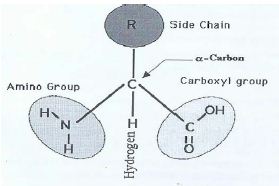
This bond is called a peptide bond and it is formed by a dehydration reaction, where a water molecule is removed. The amino group of one amino acid will bond to the carboxyl group of the next amino acid. For example the amino acid Alanine has a methyl group at this position, whereas Glycine has a hydrogen atom. Aspartic acid and asparagine, which occur in large amounts, can be synthesized by animals. The R group (also known as a side chain) is different for each of the 20 amino acids. Four amino acids, each consisting of four carbon atoms, occur in proteins they are aspartic acid, asparagine, threonine, and methionine. Their solubility depends on the size and nature of the side chain. This carbon is covalently bonded to four different groups: an amino group, a carboxyl group, a hydrogen atom, and a variable group symbolised by R. Amino acids are crystalline solids which usually are water soluble and only sparingly dissoluble in organic solvents. There are 20 different amino acids, and they all share the same general structure. In the centre of the amino acid is an assymetric carbon atom called the alpha carbon. The amino acids in a protein are bonded to each other with peptide bonds - hence the term for a polymer of amino acids is a polypeptide.
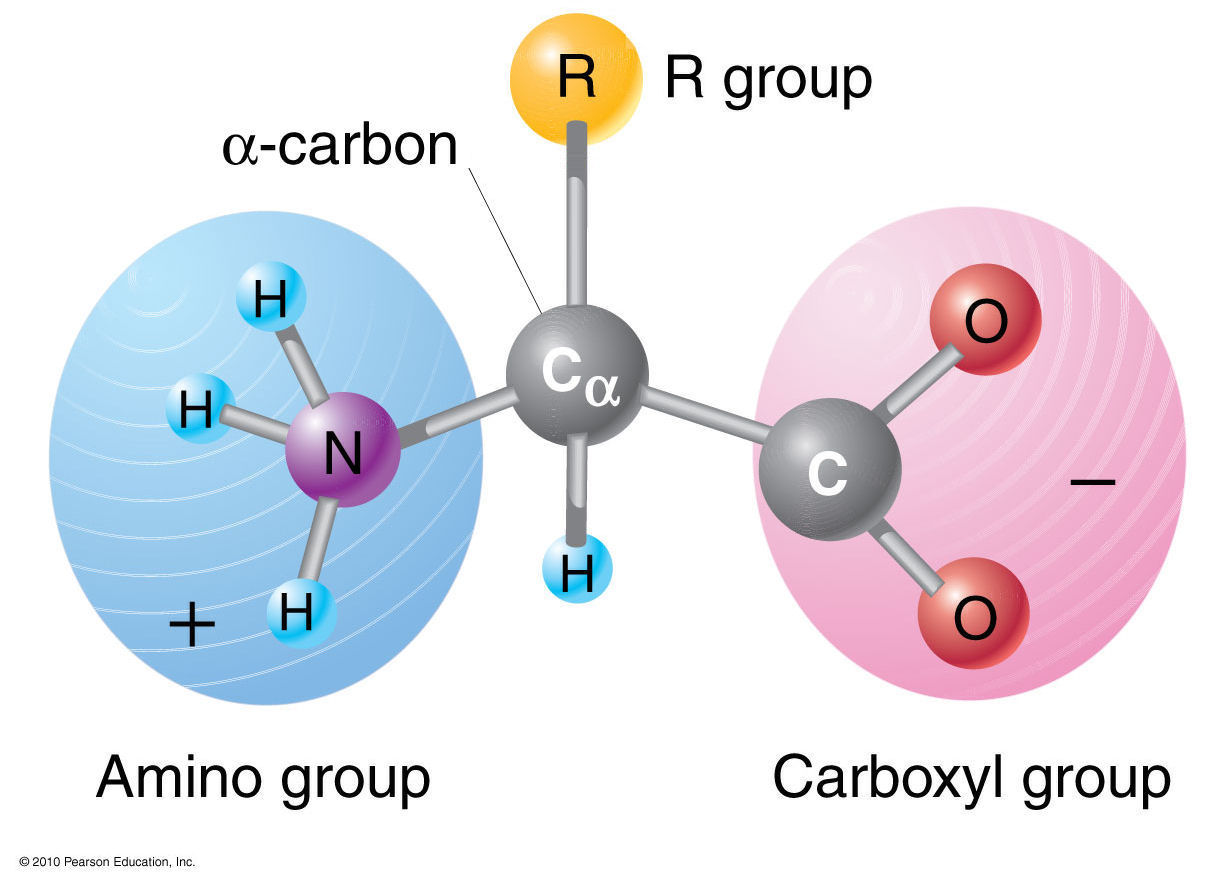
However, all these proteins are constructed from the same set of 20 amino acids, linked together in polymers. There are thousands of different proteins with diverse functions: storage, transport, structural support, cellular communication, enzymes and hormones. Refer to the charts and structures below to explore amino acid properties, types, applications, and availability. The R group for each of the amino acids will differ in structure, electrical charge, and polarity. Therefore, N will take them and become $\ce$).Proteins are made up of organic molecules called amino acids. Amino acids differ from each other with respect to their side chains, which are referred to as R groups. How does pH actually affect the amino acid? I always break it down when I explain it to my students as follows:Īn amino acid in a very protonated solution (low pH) is going to be saturated with hydrogen ions, so all molecules that can take a proton will take it as they are abundant. This form is achieved at different pH for different amino acids depending on their R groups. NotWoodward has answered it perfectly! The glycine which has both positive and negative (resulting neutral charge) is a zwitter ion form. The range of pH values at which the amino acid is zwitterionic will also vary depending on which amino acid you're looking at (the pKa values are different for every amino acid, even if only subtly) Also as Jan pointed out in the comments, other polar solvents would also allow the amino acid to show this characteristic).Īt other pH values, the molecules become singly ionised, favouring either the cationic or anionic forms.
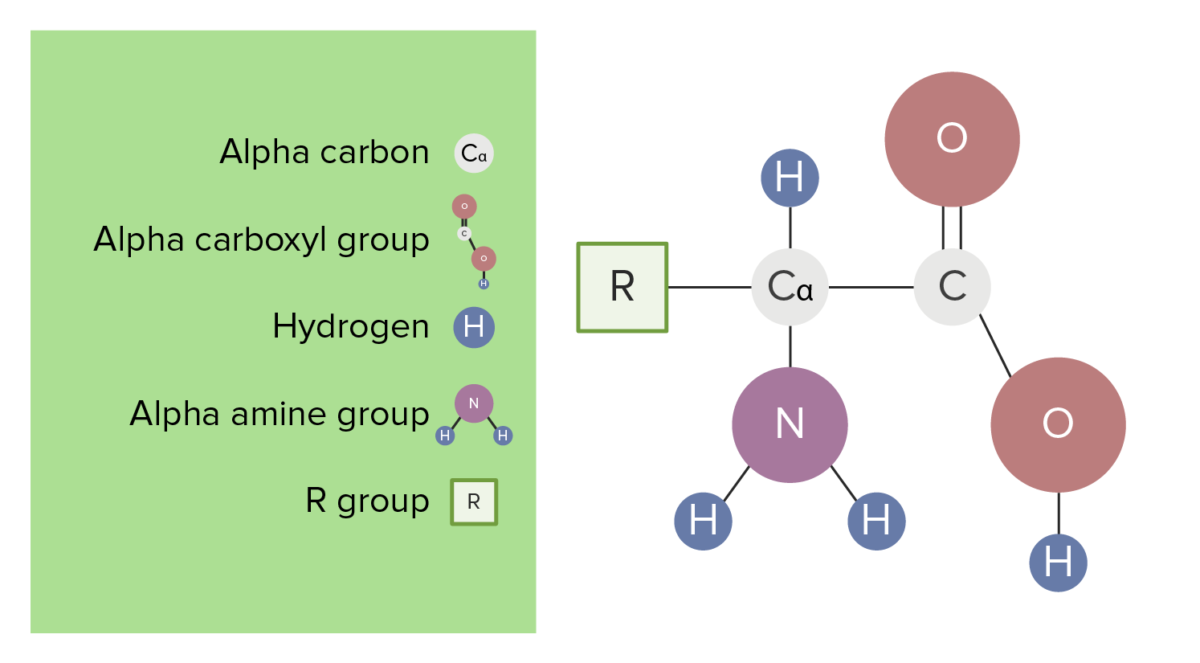
We will also discuss zwitterions, or the forms of amino acids that dominate at the isoelectric point.
#Structure of an amino acid how to#
You will learn how to calculate the isoelectric point, and the effects of pH on the amino acid's overall charge. Its worth pointing out the this property of the amino acids is valid at physiological pH for the naturally occurring amino acids, generally in aqueous medium (which living organisms have. The isoelectric point of an amino acid is the pH at which the amino acid has a neutral charge. Since amino acids contain both acidic (the carboxylic acid) and basic (the amine) moieties the molecule is able to undergo what almost appears to be an intramolecular acid-base reaction in which the acidic proton of the carboxylic acid protonates the amine, this is what gives rise to the species on the right of the image below. Dalton (Da) is an alternate name for the atomic mass unit, and kilodalton (kDa) is 1,000 daltons. is an essential amino acid with an aromatic ring d. The term amino acid is short for -amino alpha-amino carboxylic acid. Draw the structure of a naturally occurring amino acid that: a. The two forms of amino acids that your question asks about are called zwitterions (technically IUPAC says they should be called dipolar ions but the term zwitteron is pervasive). The average molecular weight of an amino acid is 110Da. amino acid, any of a group of organic molecules that consist of a basic amino group (NH 2), an acidic carboxyl group (COOH), and an organic R group (or side chain) that is unique to each amino acid.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
